Automatic, for the People
Among the various workflow automation tools around today, n8n stands out as one that has developed both a platform and a community that support users at different levels of experience. As well as its open-source software, n8n (whose unusual name comes from "nodemation", or node + automation) has built a network where developers, business users, and hobbyists exchange knowledge, report issues, and contribute to the tool’s development in terms of software development and invaluable templates for various automated processes. Founded in 2019 by Jan Oberhauser, n8n was created as an open and extensible alternative to proprietary automation platforms like Zapier. Since then, it has attracted a sizable and active community.
More recently, n8n has attracted a great deal of attention as a means of building AI agents, something for which it seems very well suited, but what has most attracted me to n8n is that as well as being a SaaS (software as a service) website, you can download the open source version which is entirely free for personal and community use (and the version reviewed here) or carries a licence fee if you want to use it in enterprise circumstances. The community version includes well over 90% of the enterprise features, but while this is theoretically usable by those new to programming and AI-building (it is, after all, distributed as a no-code/low-code platform), setting it up for AI integration requires a great deal of configuration, mainly due to the OpenAuth requirements of companies such as Google (one area where OpenAI does considerably better). If you are not especially confident in your technical abilities, you will have fewer hassles via the web site.
Nonetheless, it is worth repeating: unlike most software-as-a-service automation tools that charge on a per-task basis and keep their code proprietary, n8n gives users full access to its source code so that you can deploy it on your own infrastructure, customise it, and integrate it into existing systems. It's also a great way to explore creating AI agents, and the locally hosted version - whether enterprise or community - has proved popular with developers, businesses concerned with data privacy, and hobbyists looking for more control over their workflows. n8n works by allowing users to connect applications, services, and APIs through visual workflows. With hundreds of built-in integrations and templates available via the community forums - as well as the ability to create custom ones - the platform supports use cases from automating simple tasks like posting to social media, to managing complex data pipelines.
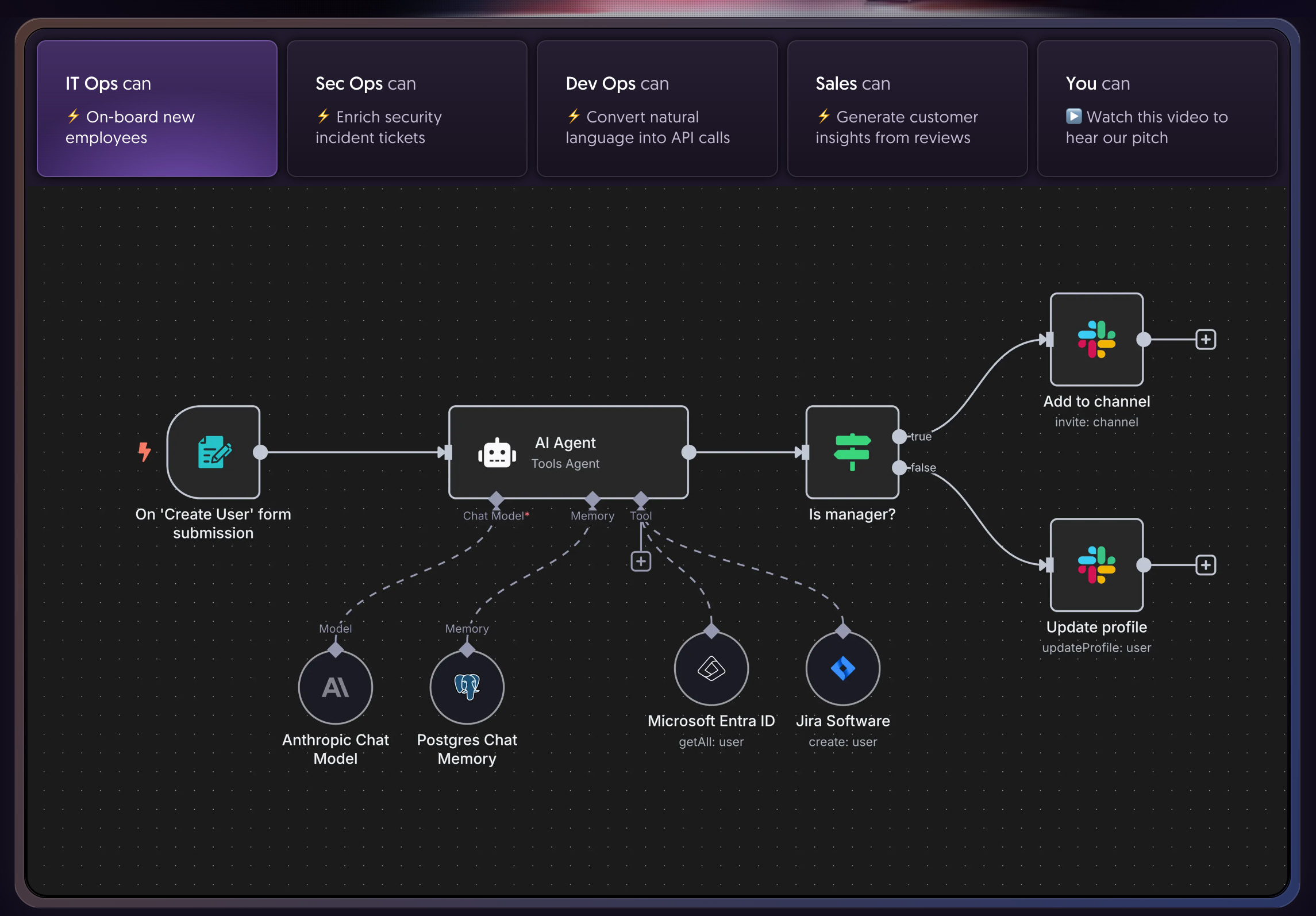
n8n works by building up nodes into a work flow that can automate a series of tasks
How does it work?
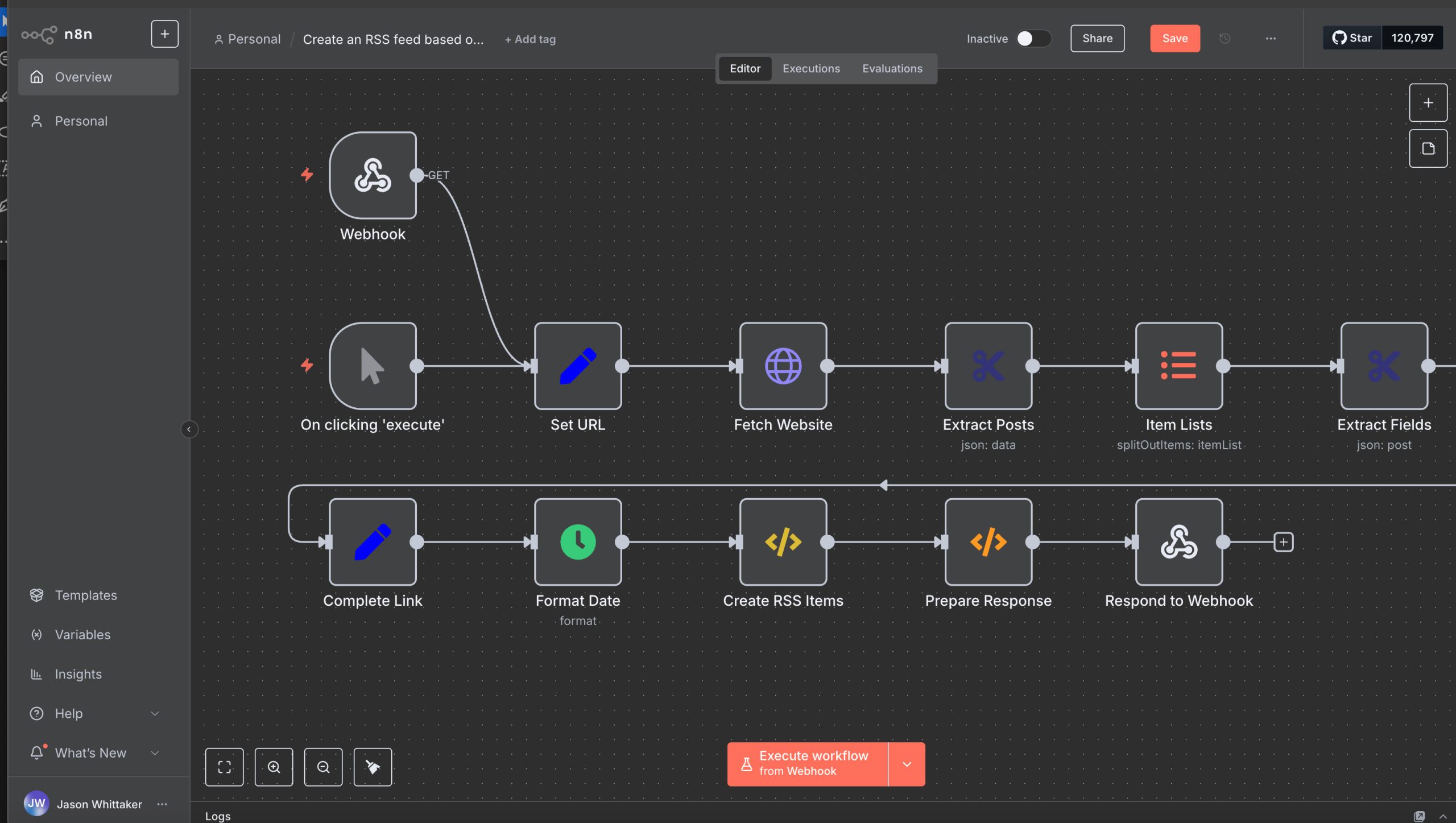
At its core, n8n is a node-based workflow automation tool. Users build workflows by dragging and dropping nodes, each of which performs a single action, then linking them to define the flow of data. You'll need some knowledge of Docker or installation via Node.js to get it up and running, so this is likely to cause some head-scratching for complete newbies, but with even with fairly basic familiarity it takes minutes to get up and running rather than hours. The reference to Node.js, a javascript runtime environment, is important as n8n allows you to get your hands dirty with coding and while theoretically you could handle all kinds of tasks without entering a line of code at all, you'll get much more out of n8n if you have some knowledge of programming.
Once installed, users access a web-based editor which is pretty much the same as that you sign into via the cloud. The editor shows a blank canvas where workflows can be built visually, with nodes representing actions, such as fetching an email, processing its content, and posting the result into a database. Each node can be configured with parameters, authentication credentials, and conditions for execution. n8n comes with more than 300 prebuilt nodes covering popular services like Slack, Google Sheets, GitHub, and AWS. Users can also create custom nodes in JavaScript or TypeScript, which extend the platform to integrate with any API or internal system. It's possible to build up simple automations in half an hour or so, or use it as a visual code developer.
Workflows can be triggered in different ways, including on a schedule, when an event occurs (via webhook or polling), or manually. Data flows between nodes as JSON, and you can manipulate it at each step using built-in functions or custom code. Advanced features include conditional logic, looping over data arrays, error handling, and parallel execution: in many respects, it works as a visual IDE, structuring coding so that you can attach it more easily to clearly identifiable elements. Workflows can also call other workflows, enabling modular designs, and n8n stores execution history and logs, which help in debugging and auditing workflows. In general, I love the user interface and while it did take me a little getting used to, the fact that so many parts are context-sensitive means that I didn't feel overwhelmed at all.
Not really for beginners
That said, if you have never used automation software before, n8n is approachable but not as immediately simple as some of its commercial competitors. Users with no experience in APIs or data formats may find it challenging, particularly if their workflows require custom logic or interactions with less common services. The visual interface is clear and makes it easy to see the sequence of steps in a workflow, while prebuilt nodes often come with templates or default settings, which help users get started. The documentation provides examples and explains core concepts like triggers, data structure, and error handling, but expect to read the fracking manual for this one, as well as the excellent community web site which contains huge amounts of genuinely helpful information.
Understanding how to work with JSON data and how to configure API credentials is often necessary, particularly for any workflows involving building AI agents, whether your own chatbots or performing RAG on local documents. Users comfortable with these concepts will find the platform flexible and powerful, and the main difficulty is less n8n's problem than that of some of the external providers: using Google's OpenAuth tools is never a joy, and this is perhaps the one area where sometimes I just wanted to click on to the web site (where the dirty work of linking your nodes to Gemini can be achieved simply by selecting a user account). For advanced use cases - such as creating custom nodes, deploying in a cluster, or integrating with private APIs - n8n assumes a higher level of technical knowledge. Self-hosting, while well-documented, requires server administration skills and some familiarity with Docker or similar tools as already noted, but even running it locally on a single machine can provide you with invaluable experience in learning how to build AI tools.
Compared to fully managed SaaS alternatives, n8n requires more setup and maintenance, especially in self-hosted deployments, and it's for this reason the Ease of Use score is so low: I actually think the interface itself, while relatively complex, can be easily mastered in a couple of hours, but ensuring that the community edition plays nicely with APIs can be a pain even for those with relevant expertise. Against this, running a locally hosted version offers more control over data, greater customizability, and no per-task pricing limits aside from those you are charged by third parties such as Google and OpenAI (the cloud version, by contrast, starts at $20 per month). The platform performs reliably under moderate load, and the execution history and error logs make it easier to troubleshoot when things go wrong. For heavy, high-frequency workflows, additional tuning and scaling may be necessary, meaning that the cloud version may be a better choice for users or teams without dedicated staff.
If you have some experience of running a server, as well as programming abilities already, the n8n Community Edition is some of the best software in this field out there, providing some incredible opportunities for creating services. I would say that strictly it's a low-coding rather than no-coding option (I say that technically it's possible to build apps without code, but mainly because I've read this rather than actually experienced it): once you're happy with that, it is a great way to start learning about AI automation.